Daily Current Affairs : 11-August-2023
Manual scavenging, a hazardous and inhumane practice, involves individuals entering sewers and manholes to clean waste, often without protective gear, jeopardizing their lives daily. In India, this practice has resulted in over 300 deaths in the last three years alone. Recognizing the urgency to eliminate this perilous occupation, the innovation of the robot ‘Bandicoot’ emerges as a crucial step towards eradicating manual scavenging and ensuring the safety and dignity of sanitation workers.
The Genesis of Bandicoot: A Collaborative Effort
In 2015, a group of engineering students from Kerala established Team Genrobotics, aiming to develop technological solutions to address societal challenges. In partnership with Kerala Startup Mission and the state’s water supply and waste-water disposal department, Genrobotics embarked on the creation of Bandicoot, a semi-automatic robot designed to revolutionize manual scavenging.
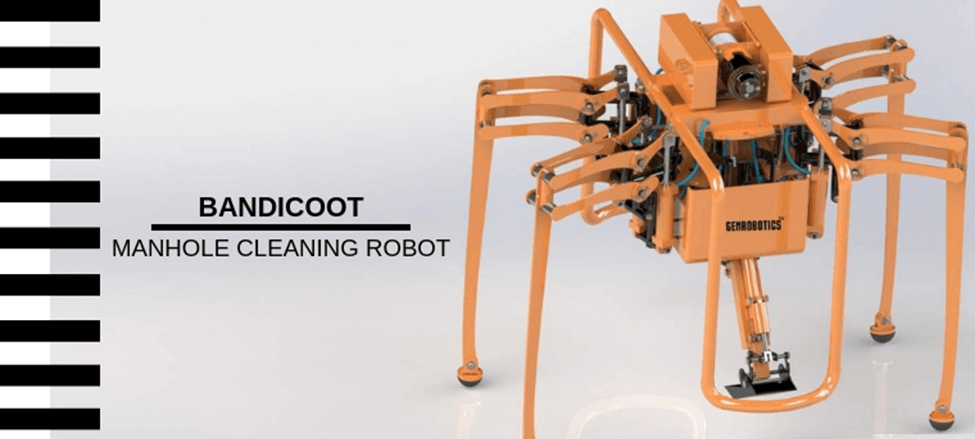
Bandicoot: Transforming the Landscape of Sanitation Work
Bandicoot is equipped with a magnetic attachment that replaces the need for workers to manually lift heavy manhole lids. This innovation not only reduces physical strain but also minimizes the risk of accidents and fatalities associated with such activities. Additionally, the robot is fitted with a camera, enabling real-time monitoring of the manhole via an operating screen. This technological breakthrough enhances the efficiency and safety of sanitation work.
Governmental Initiatives: A Legislative and Technological Push
The Manual Scavenging Act of 2013 mandates local authorities and agencies to adopt suitable technological solutions for sewer and septic tank cleaning, aiming to eradicate manual scavenging. The government also advocates the use of modern technology by providing financial incentives and assistance. To ensure the safety of sanitation workers, employers are obligated to provide safety gear and follow prescribed safety protocols.
NAMASTE Scheme: Uplifting Sanitation Workers
The NAMASTE scheme, implemented across Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India, is a comprehensive initiative with multifaceted goals:
- Zero Fatality Objective: Eliminating fatalities in sanitation work by promoting mechanized cleaning and eliminating direct contact with human waste.
- Skill Enhancement: Ensuring that sanitation work is carried out only by skilled workers, preventing untrained individuals from undertaking hazardous tasks.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness among individuals and institutions about seeking services exclusively from registered and skilled sanitation workers.
- Emergency Response: Strengthening Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs) to facilitate safe and efficient mechanized sanitation services.
- Empowerment and Formalization: Empowering sanitation workers to operate sanitation enterprises and promoting mechanization through the provision of machines, training, safety gear, and health insurance.
Important Points:
Robot ‘Bandicoot’ Technology To Eliminate Manual Scavenging
- Manual scavenging is a hazardous practice risking lives of workers.
- Over 300 manhole deaths in India in the last three years.
- Robot ‘Bandicoot’ developed to address manual scavenging issue.
Genesis of Bandicoot: A Collaborative Effort
- Founded by Kerala engineering students as Team Genrobotics.
- Collaboration with Kerala Startup Mission and state water departments.
- Aimed to create solutions for societal challenges.
Bandicoot: Transforming Sanitation Work
- Semi-automatic robot with a magnetic attachment.
- Replaces manual lifting of heavy manhole lids.
- Equipped with a camera for real-time monitoring.
- Enhances efficiency and safety of sanitation work.
Government Initiatives: A Legislative and Technological Push
- Manual Scavenging Act of 2013 mandates technological solutions.
- Government promotes modern technology with financial incentives.
- Employers must provide safety gear and follow safety protocols.
NAMASTE Scheme: Uplifting Sanitation Workers
- Implemented in Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) across India.
- Objectives: zero fatalities, skilled workers, public awareness.
- Strengthening Emergency Response Sanitation Units (ERSUs).
- Empowerment of sanitation workers, mechanization, health insurance.
Why In News
Introducing the revolutionary ‘Bandicoot’ robot, poised to eradicate the hazardous practice of manual scavenging. With its advanced technology, Bandicoot is set to transform waste management and ensure a safer, more dignified future for sanitation workers worldwide.
MCQs about The Bandicoot Robot and NAMASTE Scheme’s Impact
-
The primary purpose of the Bandicoot robot is:
A. To monitor traffic in urban areas.
B. To provide entertainment at public events.
C. To eliminate manual scavenging and enhance sanitation work.
D. To assist in agricultural activities.
-
Which government initiative aims to ensure zero fatalities in sanitation work and promote mechanization of cleaning operations?
A. Clean India Campaign
B. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
C. NAMASTE Scheme
D. Sanitation Empowerment Program
-
How does the Bandicoot robot contribute to safer sanitation work?
A. It provides entertainment for sanitation workers.
B. It replaces skilled sanitation workers.
C. It uses a magnetic attachment to lift heavy manhole lids.
D. It operates without any monitoring equipment.
-
What is the Manual Scavenging Act of 2013 in India aimed at?
A. Promoting traditional sanitation practices.
B. Encouraging manual scavenging as a profession.
C. Providing safety gear to all workers.
D. Mandating the use of appropriate technological solutions to eliminate manual scavenging.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


