Hindu Editorial Analysis : 1-January-2024
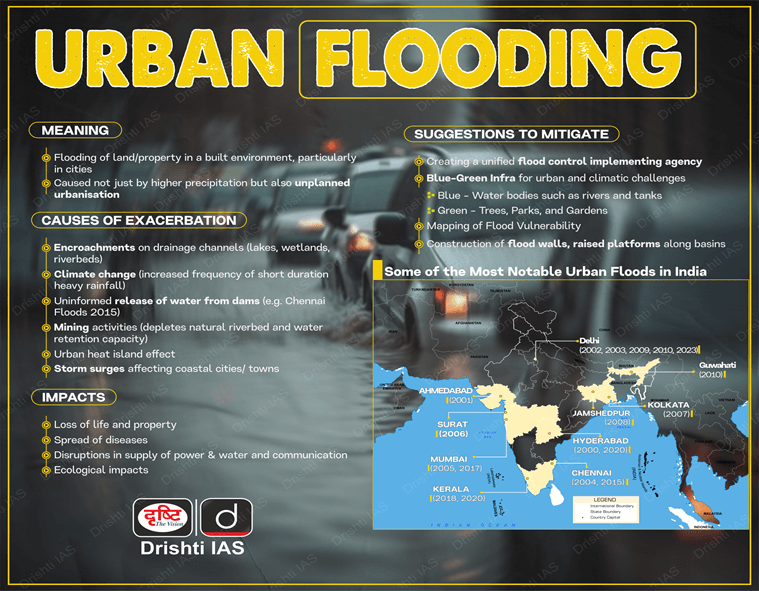
Urban flooding has become a pressing issue in India, exacerbated by factors such as climate change, unplanned urban growth, and inadequate drainage systems. The aftermath of Cyclone Michuang underscores the urgent need for preventive measures.
Causes of Urban Floods:
- Weather Systems:
- Heavy monsoon rainfall, cyclones, cyclonic circulations, and cloud bursts contribute to flash floods.
- Storm surges pose a threat to coastal cities and towns.
- Precipitation:
- Monsoon months witness 80% of precipitation, leading to heavy sediment loads and drainage congestion.
- Sudden water release from dams exacerbates flooding.
- Urban Heat Island:
- Increased rainfall over urban areas due to the urban heat island effect.
- Climate Change & Sea Level Rise:
- Altered weather patterns and intensified rainfall events affect cities located on coasts, riverbanks, and hilly areas.
Urban Challenges & Floods in India:
- Encroachment & Habitations:
- Unplanned urban growth and encroachment hinder natural drainage systems.
- Loss of Drains:
- Inadequate maintenance and widening of natural drains contribute to flooding.
- Improper disposal systems:
- Inefficient waste disposal reduces the carrying capacity of drains.
- Health Risk:
- Floods increase the risk of infectious diseases, posing health challenges.
- Insufficient policy attention:
- Historically, urban flooding has not received adequate planning and attention.
Solutions:
- Nature-based Solutions:
- Wetland, river, lake, and mangrove restoration.
- Bioremediation of water bodies.
- Rainwater harvesting techniques.
- Permeable Ground Surfaces:
- Increasing permeable surfaces to reduce surface runoff.
- Planning Interventions:
- Urban River Management Plan.
- River Basin Management Plan.
- Flood Resilience Strategy.
- Interlinking rivers and canals.
- Community-based Flood Management Plan.
Government Efforts:
- Urban Flood Mitigation Project:
- A Rs 561 crore project under the National Disaster Mitigation Fund.
- Master Plan for Artificial Recharge to Groundwater – 2020:
- Envisages the construction of rainwater harvesting structures.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA):
- Focuses on rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge.
- Amrit Sarovar Mission:
- Aims to develop and rejuvenate water bodies for rainwater harvesting.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana:
- Emphasizes demand-side management of groundwater.
- AMRUT 2.0 Scheme:
- Provisions for rainwater harvesting through stormwater drains.
Why In News
After the landfall of Cyclone Michuang, there is a pressing need to take preventive measures and implement sustainable urban planning strategies to mitigate the risk of flooding in India’s urban areas and ensure the resilience of vulnerable communities.
MCQs about Urban Flooding in India
-
According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), how much have flood-related catastrophes increased since 2000 compared to the two previous decades?
A. 50%
B. 75%
C. 100%
D. 134%
-
What is a nature-based solution mentioned in the essay for mitigating urban flooding?
A. Increasing impermeable surfaces
B. Building more dams
C. Wetland restoration
D. Disposal of construction debris
-
Which government initiative aims to address urban flooding through rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge?
A. National Disaster Mitigation Fund
B. Atal Bhujal Yojana
C. Urban River Management Plan
D. Jal Shakti Abhiyan
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


