Daily Current Affairs : 4-August-2023
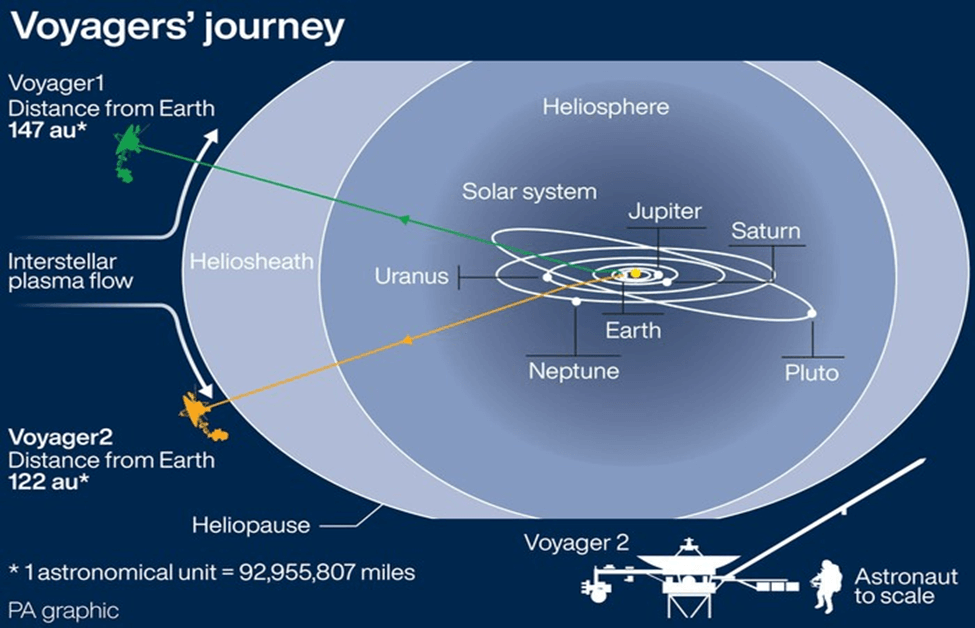
In recent news, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) faced a temporary setback in its communication with a stalwart traveler of the cosmos, Voyager 2. This remarkable space probe, a symbol of human curiosity and ingenuity, has been venturing through the universe for approximately 46 years, shedding light on the mysteries of interstellar space. Let’s delve into the mission, its objectives, and the unique features of the Voyager spacecraft.
Embarking on a Bold Odyssey: The Voyager Mission
Launched nearly five decades ago, Voyager 2 stands as a testament to humanity’s ceaseless pursuit of knowledge and exploration. It is the second spacecraft to traverse the vast expanse of interstellar space, a region lying beyond the constant influence of our Sun’s material and magnetic forces. The pioneering spirit of this mission is magnified when we consider that its predecessor, Voyager 1, was launched a mere two weeks before Voyager 2, making them simultaneous emissaries of our species into the cosmic unknown.
A Celestial Tour: Voyager’s Scientific Endeavors
The Voyager duo embarked on an unprecedented expedition, offering us a front-row seat to the grandeur of our solar system’s outer giants. Their journey allowed us to uncover the secrets of distant planets and their cosmic companions. Notably, the probes’ inquisitive gaze led to the discovery of more than 40 moons and a plethora of enigmatic rings encircling these distant worlds. Through their lens, we witnessed the majesty of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, unveiling the intricate dance of celestial bodies that had previously remained concealed from our view.
Instruments of Discovery: Unveiling the Voyager Craft
At the heart of the Voyager spacecraft’s remarkable achievements lies a suite of cutting-edge instruments, each meticulously designed to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos. These tools facilitated the execution of ten distinct experiments, effectively transforming the probes into versatile scientific platforms. The arsenal of exploration included:
- Television Cameras: These lenses captured captivating images of planets and other celestial entities, allowing us to gaze upon the raw beauty of distant worlds.
- Infrared and Ultraviolet Sensors: These detectors unveiled the hidden spectral signatures of cosmic phenomena, shedding light on the composition and characteristics of the objects encountered.
- Magnetometers: Voyager’s magnetic sensors unveiled the intricate magnetic landscapes of planets, unraveling the forces shaping their atmospheres and geologies.
- Plasma Detectors: These instruments played a crucial role in studying the charged particles that populate the space between planets, offering insights into the dynamic interplay of solar winds and cosmic environments.
- Cosmic-Ray and Charged-Particle Sensors: By scrutinizing the flux of high-energy particles, Voyager enhanced our understanding of the harsh cosmic radiation permeating interstellar space.
Powering the Journey: Navigating Beyond Solar Limits
In a departure from the norm, the Voyager spacecraft broke free from reliance on solar power as they ventured into the distant reaches of space. Unlike their solar-powered counterparts, these pioneers harnessed the energy generated by a compact nuclear power plant. This ingenious system drew upon the controlled radioactive decay of a plutonium pellet, providing the probes with a steady supply of hundreds of watts, ensuring their continued operation even in the depths of space’s cold and darkness.
Important Points:
- Embarking on a Bold Odyssey: The Voyager Mission
- Launched 46 years ago, second spacecraft to enter interstellar space.
- Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 launched two weeks apart.
- A Celestial Tour: Voyager’s Scientific Endeavors
- Explored outer giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
- Discovered over 40 moons, numerous rings.
- Instruments of Discovery: Unveiling the Voyager Craft
- Equipped with 10 different instruments.
- Instruments include television cameras, infrared and ultraviolet sensors, magnetometers, plasma detectors, cosmic-ray, and charged-particle sensors.
- Powering the Journey: Navigating Beyond Solar Limits
- Not powered by solar energy like other spacecraft.
- Relies on a small nuclear power plant.
- Uses plutonium pellet for energy generation.
Why In News
Recently, NASA experienced a disheartening moment as communication with Voyager 2, Earth’s longest-running space probe, was temporarily lost. Despite this setback, the dedicated team at NASA is diligently working to reestablish contact and continue the remarkable journey of Voyager 2, further unraveling the mysteries of our cosmos.
MCQs about Voyager 2
-
What was the primary objective of Voyager 2’s mission?
A. To study the behavior of birds in space.
B. To capture high-resolution images of distant galaxies.
C. To analyze the composition of interstellar gases.
D. To explore outer planets and enter interstellar space.
-
How is Voyager 2 powered, and what makes its power source unique?
A. It is powered by solar panels and batteries.
B. It relies on wind energy from cosmic winds.
C. It uses a nuclear power plant fueled by plutonium.
D. It generates energy from the gravitational pull of planets.
-
What major discoveries did the Voyager spacecraft make during their mission?
A. New galaxies beyond our Milky Way.
B. Over 100 moons orbiting Jupiter and Saturn.
C. The secret behind black holes.
D. More than 40 moons and numerous rings around outer planets.
Boost up your confidence by appearing our Weekly Current Affairs Multiple Choice Questions
![]()


